Grid Reference
The byugrid library helps you learn to program by using a 2-dimensional grid.
You can think of the grid as a set of cells, indexed by x values along the
horizontal axis (left to right) and y values along the vertical axis (top to
bottom).
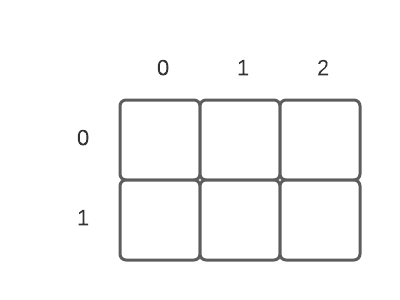
Each cell can hold an arbitrary value, such as an integer or a string.
Installing the grid library
The most reliable way to install byugrid is through PyCharm. Open the
File->Settings (Windows) or File->Preferences (MacOS) menu and select
Project. You should see a your Conda environment and a list of packages
installed in that environment:

Click the + and then type in byugrid. Then click Install Package.
Alternatively, you can type pip install byugrid in a PyCharm terminal. Be sure
that terminal is using the CS 110 environment.
Importing the grid library
To use the Grid, you always need to import it using the following:
from byugrid import GridCreating a grid
You can create a grid in two ways:
-
Grid(width, height)— creates a new grid whose size is given by width and height (width specifies columns and height specifies rows) -
Grid.build(rows)— creates a new grid using the supplied rows.
In the first case, we can create a blank grid:
grid = Grid(3, 2)This creates a new Grid, like the one shown above, that is 3 columns wide and 2
rows high. The value of each cell is None. The world is stored in a variable
called grid.
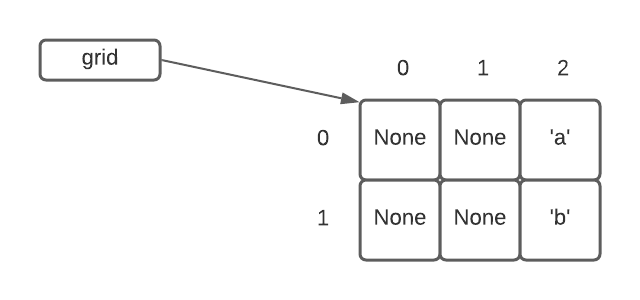
In the second case, we can create a grid by specifying every value:
grid = Grid.build([[None, None, 'a'], [None, None, 'b']])This creates a grid that looks like this:
Grid height and width
You can get the grid width and height using the following:
grid.width— grid width in cellsgrid.height— grid height in cells
You can use these to loop over the rows and columns. For example:
# loop over all the columns
for x in range(grid.width)
# loop over all the rows
for y in range(grid.height)Getting and setting cell contents
You can get and set cell contents using the following:
grid.get(x, y)— get the contents of the cell at coordinate (x, y)grid.set(x, y, value)— set the contents of the cell at coordinate (x, y) to contain the supplied value
For example:
# gets the value at (1, 2)
value = grid.get(1, 2)
# sets the value at (3, 4) to contain 'hello'
grid.set(3, 4, 'hello')Checking if a coordinate is in bounds
If you try to get or set a coordinate that is not in bounds, you will cause a Python error. Before getting or setting a coordinate, you can check if it is in bounds using:
grid.in_bounds(x, y)— returns True if the coordinate is in bounds, False otherwise
Cheat Sheat
from byugrid import Grid- Create
Grid(width, height)— creates a new, blank gridGrid.build(rows)— creates a new grid using the supplied rows, e.g.Grid.build([[None, None, 'a'], [None, None, 'b']])
- Width and height
grid.width— grid width in cellsgrid.height— grid height in cells
- Looping over pixels
for x in range(grid.width):— loop over all columnsfor y range(grid.height):— loop over all rows
- Getting and setting cell contents
grid.get(x, y)— get the contents of the cell at coordinate (x, y)grid.set(x, y, value)— set the contents of the cell at coordinate (x, y) to contain the supplied value
- Bounds checking
grid.in_bounds(x, y)— returns True if the coordinate is in bounds, False otherwise